See: exopodite [Martin, 2005].
(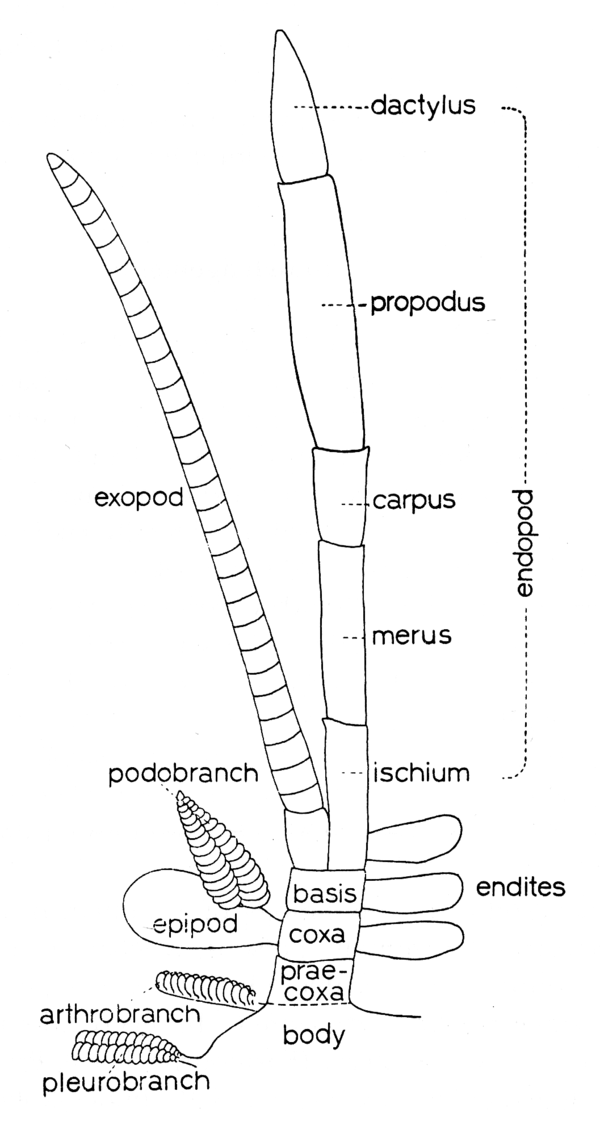 ) [Holthuis, 1993].
) [Holthuis, 1993].
 ) [Holthuis, 1993].
) [Holthuis, 1993].Schematic drawing of a thoracic leg. [Holthuis, 1993]
Lateral of two rami arising from the protopod and constituting the biramous limb [Brusca and Brusca, 2002].
Lateral ramus of a biramus appendage, arising from the basis, or from the protopodite (Fig. 3C) [Perez Farfante and Kensley, 1997].
Lateral ramus of biramus appendage, originating on second segment (basis) from base (see Fig. 13) [Hobbs and Jass, 1988].
Outer branch of a biramous appendage [Ingle, 1980].
Outer of two branches of biramous limb, comprising one or several short articles arising from basis; absent from many limbs. (Syn. exopodite) [Poore, 2004].
Outer ramus of limb arising from protopod basis; may contain variable number of segments or be much reduced or lacking [Moore and McCormick, 1969].
The lateral branch of a bifurcate appendage arising from the basis or from the protopodite [Chace and Hobbs, 1969].
The lateral or exterior ramus of a crustacean basis. In the Isopoda, applied to the outer ramus of a pleopod or uropod [Wilson, 1989].
The lateral ramus of a biramous appendage, having its origin on the basis [Hobbs, Hobbs, and Daniel 1977].
The outer of two branches of the primitive appendage (Fig. 2) [Warner, 1977].
(Order Cladocera):
Lobe-like outer branch (ramus) of trunk appendage; lacks articulation with protopodal part of appendage. Reduced in certain predatory water fleas. (Syn. exopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].
(Order Notostraca):
Large, setose outer lobe of thoracic appendage (thoracopod) ot abdominal appendage. Extends dorsally and ventrally from narrow point of attachment; modified on last (11th) thoracopods in female to form ovisac. (Syn. exopodite, flabellum) [Stachowitsch, 1992].
(Order Diplostraca):
Outer branch of trunk appendage; unsegmented, prolonged dorsally and ventrally, and bearing marginal setae. Dorsal extension occasionally interpreted as representing additional epipod or flabellum, ventral extension as exopod proper. (Syn. exopodite, flabellum) [Stachowitsch, 1992].
(Order Anostraca):
Outer branch of thoracic appendage (thoracopod). Unsegmented, lobe-like, and bearing marginal setae; articulated with protopod. Serves in locomotion. (See also endopod). (Syn. exopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].
(Class Cephalocarida):
Outer branch of biramous appendage. Refers to annulate outer branch of antennae, six-segmented branch (in larvae only) of mandibles, one-segmented branch of maxillules, as well as two-segmented branches of maxillae and thoracopods. (See also endopod). (Syn. exopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].
(Order Cumacea):
Outer branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. Represents small branch of pereopods; occasionally interpreted as representing flabellum of maxilla as well as siphonal lobe of of first maxillipeds. (Syn. exopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].
(Order Tanaidacea):
Outer branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. May be present as small ramus on chelipeds and anterior pereopods. Scale-like projection (antennal scale) on antenna considered to represent exopod. (Syn. exopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].
(Order Decapoda):
Outer branch (ramus) of biramous appendage (endopod, exopod). Refers to antennal scale (scaphocerite) of antenna, scaphognathite of maxillula, flagelliform branch of maxillipeds, and variously developed outer branch of pereopods, pleo-pods, and uropods. (annulate, flagelliform, scale-like, spine-like). (Syn. exopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].
(Order Amphipoda):
Outer branch (ramus) of biramous appendage (e.g., pleopod, uropod). (Syn. exopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].
(Order Isopoda):
Outer (lateral) ramus of an appendage [Wetzer et al. 1997].
(Order Isopoda):
(Order Isopoda):
Outer ramus of a paired appendage [Kensley and Schotte, 1989].
(Order Mysida):
Outer branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. Represents scale-like structure (antennal scale) of antenna and flagellum-shaped branch of maxilipeds, thoracopods, and pleopods. (annulate, elongate, flattened; natatory; reduced). (Syn. exopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].
(Order Stomatopoda):
Outer branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. Refers to twosegmented branch of antennae, one-segmented, gill-bearing branch of pleopods, and twosegmented branch of uropods, while it is considered to represent inner branch of last three thoracopods. (See also endopod). (Syn. exopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].
(Order Leptostraca):
Outer branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. (elongate and slender, flattened = lamellar = scale-like = plate-like). (Syn. exopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].
(Subclass Branchiura):
Setose outer branch (ramus) of thoracic appendage (thoracopod). Exopod of first two thoracopods may bear medially directed flabellum. (See also endopod) [Stachowitsch, 1992].
(Subclass Cirripedia):
(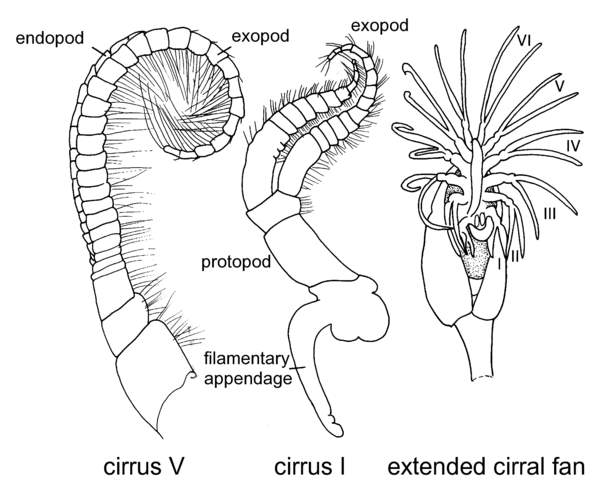 ) [Anderson, 1980].
) [Anderson, 1980].
 ) [Anderson, 1980].
) [Anderson, 1980].Lepas anatifera: cirrus V; cirrus I, and extended cirral fan. [Anderson, 1980]
(Subclass Cirripedia):
Outer branch (ramus) of thoracic appendage (thoracopod in ascothoracican, cirrus in other cirripeds). (one- to three-jointed, multiarticulate) (see also endopod). (Syn. exopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].
(Subclass Copepoda):
A dorsal extension of the proximodistal axis of a limb originating on the basis of the protopod and usually segmented. Segments of the exopod bear a dorsal seta and often a ventral seta, but usually there is only one of each kind of seta on a segment [Ferrari and Dahms, in press].
(Subclass Copepoda):
Outer branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. Refers to outer branch of antenna (occasionally reduced), mandible, maxillule, and pereopod. (See also endopod). (Syn. exopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].
(Subclass Copepoda):
The outer ramus of a biramous appendage [Boxshall and Halsey, 2004].
(Subclass Mystacocarida):
Out branch of biramous appendage. Refers to ninesegmented branch of antenna, seven-segmented branch of mandible, and one-segmented branch of maxilliped. (See also endopod). (Syn. exopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].
(Class Ostracoda):
In distally biramous crustacean limb, the lateral ramus. (Syn. exopodite) [Cohen, Peterson, and Maddocks, in press].
(Class Ostracoda):
Outer branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. Often developed as a branchial plate. (See also endopod). (Syn. exopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].
(Class Remipedia):
Outer or more dorsal branch (ramus) of biramous appendage (antennule, antenna, trunk limb). (Syn. exopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].
(Superorder Syncarida):
Outer branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. In anaspidacean, representing scale-like branch (scaphocerite) of antenna (also occasionally in bathynellacean) and annulated ramus of thoracopods. (annulate, scale-shaped, spatulate, styliform). (Syn. exopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].
(Order Thermosbaenacea):
Outer branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. Present as small lobe on maxillae, palp-like structure of maxilliped, smaller, one- to two-segmented ramus of thoracopods, and two-segmented remud of uropod. (Syn. exopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].
(Order Euphausiacea):
Outer branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. Represents scale (scaphocerite) of antenna, one-segmented lobe of maxilla in certain euphausiaceans, relatively small, two-segmented outer branch of thoracopods, and flattened outer branch of pleopods and uropods. (Syn. exopodite) See: endopod [Stachowitsch, 1992].
Crustacea glossary. Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County. 2011.