- afibrillar c. c. which, with the electron microscope, appears as laminated, electron-dense reticular material that sometimes overlies the enamel of the tooth.
- primary c. c. that has no cementocytes; may cover the entire root of the tooth, but often is missing on the apical third of the root.
* * *
ce·men·tum si-'ment-əm n a specialized external bony layer covering the dentin of the part of a tooth normally within the gum called also cement compare DENTIN, ENAMEL
* * *
(cement)
n.
a thin layer of hard tissue on the surface of the root of a tooth. It attaches the fibres of the periodontal membrane to the tooth.
* * *
ce·men·tum (sə-menґtəm) [L. caementum rough stone] [TA] the bonelike, rigid connective tissue covering the root of a tooth from the cementoenamel junction to the apex and lining the apex of the root canal; it also serves as an attachment structure for the periodontal ligament, thus assisting in tooth support. Called also substantia ossea dentis.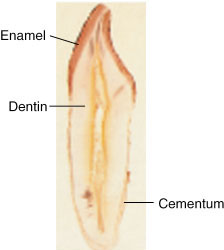
 Cementum covering the anatomical root, thickening toward the apical region, in a ground longitudinal section of a tooth. The dental pulp has been lost in preparation.
Cementum covering the anatomical root, thickening toward the apical region, in a ground longitudinal section of a tooth. The dental pulp has been lost in preparation.
Medical dictionary. 2011.