Emission of a longer wavelength radiation by a substance as a consequence of absorption of energy from a shorter wavelength radiation, continuing only as long as the stimulus is present; distinguished from phosphorescence, which emission persists for a perceptible period of time after the stimulus has been removed. See photoelectric effect. [fluorspar + -escence, inchoative suffix]
* * *
flu·o·res·cence -'es-ən(t)s n luminescence that is caused by the absorption of radiation at one wavelength followed by nearly immediate reradiation usu. at a different wavelength and that ceases almost immediately when the incident radiation stops also the radiation emitted
flu·o·res·cent -'es-ənt adj
* * *
n.
the emission of light by a material as it absorbs radiation from outside. The radiation absorbed may be visible or invisible (e.g. ultraviolet rays or X-rays).
• fluorescent adj.
* * *
flu·o·res·cence (fl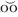 -resґəns) [first observed in fluorspar] the property of emitting light while exposed to light, the wavelength of the emitted light being only slightly longer than that of the light absorbed. Cf. phosphorescence.
-resґəns) [first observed in fluorspar] the property of emitting light while exposed to light, the wavelength of the emitted light being only slightly longer than that of the light absorbed. Cf. phosphorescence.
Medical dictionary. 2011.