* * *
One of two subdivisions of the trachea serving to convey air to and from the lungs. The trachea divides into right and left main bronchi, which in turn form lobar, segmental, and intrasegmental bronchi. In structure, the intrapulmonary bronchi have a lining of pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium and a lamina propria with abundant longitudinal networks of elastic fibers; there are spirally arranged bundles of smooth muscle, abundant mucoserous glands, and, in the outer part of the wall, irregular plates of hyaline cartilage. SYN: bronchium. [Mod. L., fr. G. bronchos, windpipe]
- hyparterial bronchi those bronchi that pass below the pulmonary arteries, i.e., right middle and inferior lobar bronchi and left superior and inferior lobar bronchi.
- intermediate b. the portion of the right main b. between the upper lobar b. and the origin of the middle and lower lobar bronchi. SYN: b. intermedius.
- b. intermedius SYN: intermediate b..
- intrasegmental bronchi [TA] branches of segmental bronchi to the bronchopulmonary segments of the lungs. SYN: bronchi intrasegmentales [TA], branches of segmental bronchi, rami bronchiales segmentorum.
- bronchi intrasegmentales [TA] SYN: intrasegmental bronchi.
- left main b. [TA] it arises at the bifurcation of the trachea, passes in front of the esophagus and enters the hilum of the left lung where it divides into a superior lobe b. and an inferior lobe b.. It is longer, of narrower caliber, and more nearly horizontal than the right main b., hence, aspirated objects enter it less frequently. SYN: b. principalis sinister [TA].
- lobar bronchi [TA] the divisions of the main bronchi that supply the lobes of the lungs; superior lobar bronchi (b. lobaris superior [TA]); middle lobar bronchi (b. lobaris medius [TA]); and inferior lobar bronchi (b. lobaris inferior [TA]) are the three lobar bronchi on the right; superior lobar bronchi (b. lobaris superior [TA]) and inferior lobar bronchi (b. lobaris inferior [TA]) are the two on the left. The lobar bronchi divide into segmental bronchi. SYN: bronchi lobares [TA].
- bronchi lobares [TA] SYN: lobar bronchi.
- mucoid impaction of b. plugging of the lumen of bronchi due to thickened mucus, interfering with ventilation of corresponding lung segments and leading to characteristic clustered linear and grapelike radiologic densities and occasionally atelectasis and pneumonia; characteristically seen in cystic fibrosis but it can occur in a variety of disease states.
- primary b. the main b. arising at the tracheal bifurcation and extending into the developing lung of the embryo.
- right main b. [TA] it arises at the bifurcation of the trachea and enters the hilum of the right lung, giving off the superior lobe b. and continuing downward to give off the middle and inferior lobe bronchi. It is shorter, of greater caliber, and more nearly vertical than the left main b., thus, aspirated objects more frequently lodge on the right side. SYN: b. principalis dexter [TA].
- segmental b. [TA] one of the divisions of the lobar b. that supplies a bronchopulmonary segment. In the right lung there are commonly ten: in the superior lobe, the apical (B1) segmental b., b. segmentalis apicalis (BI) [TA]; posterior (B2) segmental b., b. segmentalis posterior (BII) [TA]; and anterior (B3) segmental b., b. segmentalis anterior (BIII) [TA]; in the middle lobe, lateral (B4) segmental b., b. segmentalis lateralis (BIV) [TA]; and medial (B5) segmental b., b. segmentalis medialis (BV) [TA]; in the inferior lobe, superior (B6) segmental b., b. segmentalis superior (BVI) [TA], medial basal (B7) segmental b., b. segmentalis basalis medialis (BVII) [TA]; anterior basal (B8) segmental b., b. segmentalis basalis anterior (BVIII) [TA]; lateral basal (B9) segmental b., b. segmentalis basalis lateralis (BIX) [TA]; and posterior basal (B10) segmental b., b. segmentalis basalis posterior (BX) [TA]. In the left lung there are commonly nine: in the superior lobe, the apicoposterior (B1+2) segmental b., b. segmentalis apicoposterior (BI+II) [TA]; anterior (B3) segmental b., b. segmentalis anterior (BIII) [TA]; superior lingular (B4) segmental b., b. lingularis superior (BIV) [TA]; and inferior lingular (B5) segmental b., b. lingularis inferior (BV) [NA]; in the inferior lobe, superior (B6) segmental b., b. segmentalis superior (BVI) [TA]; medial basal (B7) segmental b., b. segmentalis basalis medialis (cardiacus) (BVII) [TA], anterior basal (B8) segmental b., b. segmentalis basalis anterior (BVIII) [TA]; lateral basal (B9) segmental b., b. segmentalis basalis lateralis (BIX) [TA]; and posterior basal (B10) segmental b., b. segmentalis basalis posterior (BX) [TA]. SYN: b. segmentalis [TA].
- b. segmentalis [TA] SYN: segmental b..
* * *
bron·chus 'bräŋ-kəs n, pl bron·chi 'bräŋ-.kī, -.kē either of the two primary divisions of the trachea that lead respectively into the right and the left lung broadly BRONCHIAL TUBE
* * *
n. (pl. bronchi)
any of the air passages beyond the trachea (windpipe) that has cartilage and mucous glands in its wall. The trachea divides into two main bronchi, which divide successively into five lobar bronchi, 20 segmental bronchi, and two or three more divisions. See also bronchiole.
• bronchial adj.
* * *
bron·chus (brongґkəs) pl. bronґchi [L., from Gr. bronchos windpipe] [TA] any of the larger air passages of the lungs, having an outer fibrous coat with irregularly placed plates of hyaline cartilage, an interlacing network of smooth muscle, and a mucous membrane of columnar ciliated epithelial cells. bronchial adj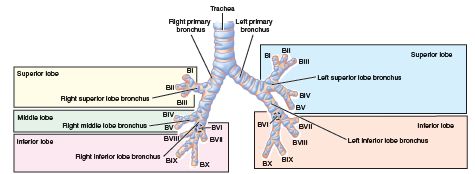
 Bronchi, showing primary, lobar, and segmental bronchi, which connect to the bronchopulmonary segments (S I–X) of the right and left lungs. For correlation of the bronchopulmonary segments with subdivisions of the lungs, see Plate 27.
Bronchi, showing primary, lobar, and segmental bronchi, which connect to the bronchopulmonary segments (S I–X) of the right and left lungs. For correlation of the bronchopulmonary segments with subdivisions of the lungs, see Plate 27.
Medical dictionary. 2011.